Where Is Burkina Faso?
Slightly larger than Colorado, Burkina Faso is a land locked country nestled alongside Mali’s eastern border. Its other neighbors are Niger, Benin, Togo, Ghana, and the Ivory Coast. The country consists of extensive plains, low hills, high savannas, and the Sahara Desert.
Burkina Faso means “Land of the honest men” or also interpreted as “country of incorruptible people.” The capital is Ouagadougou, sometimes shortened to Ouaga, means “You are welcome here at home with us.” People from Burkina Faso are called Burkinabé (pronounced burr-KEE-na-bay). It is one the poorest countries in the world with around 44% of its population living under the poverty line. Burkina Faso has a very young population with more than 65% of the people under the age of 25.
Burkina Faso was formerly known as the Upper Volta named after its three major rivers the Black, Red, and White Voltas that flow from the open plateaus of Bobo-Dioulasso highlands to Ghana. It is home to about 60 ethnic groups, the Mossi being the biggest one with about 50%. The country’s history dates back to pre-historic times. There are artifacts proving that Burkina Faso is actually home to one of the oldest human settlements in West Africa when people were hunter gatherers and later became farmers. Traditional beliefs hold that crocodiles and humans share the same spirit. Therefore, the animal is sacred and often hand fed.
Watch a video of the sacred animal:


Climate Challenges:
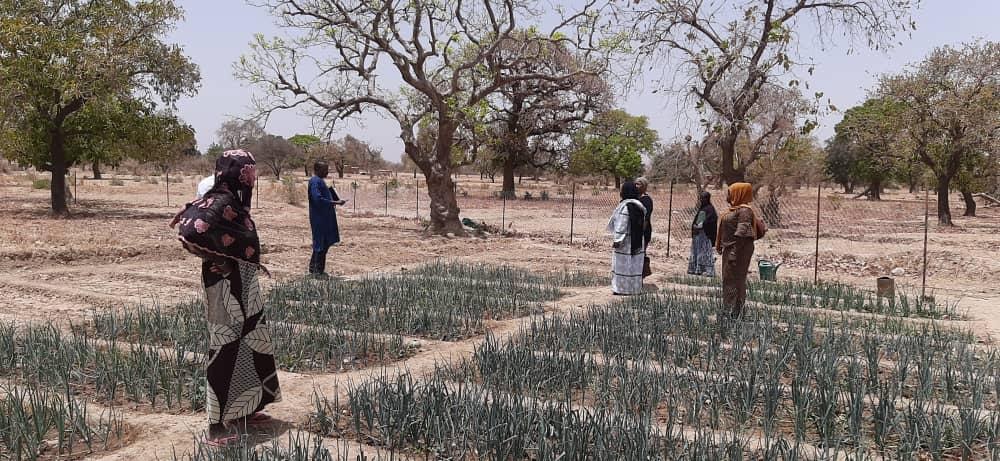
Burkinabe people rely on subsistence agriculture. Subsistence agriculture is essentially farming to produce crops people can live off. Over 80% of the population relies on this to survive. Agriculture accounts for 90% of the countries production and includes cotton, peanuts, shea nuts, sesame, sorghum, millet, corn, rice and livestock. The main exports are cotton referred to as “white gold,” livestock, and gold. Cotton exports are dominant and represent about 60 percent of total agricultural exports.
The reliance on farming is problematic as the climate of Burkina Faso makes it vulnerable to extended periods of drought resulting in land degradation, deforestation and desertification. The agriculture-based economy is characterized by low crop and livestock productivity, minimal diversification, and limited agro-pastoral value-chains. While improvements have greatly reduced the threat of recurring famine, more than 3.5 million people, roughly 20 percent of the population, are food insecure. Seasonal employment migration to neighboring countries is common.
Still, Burkina has a potential comparative advantage in several non-traditional cash crops, such as fruit (especially mangoes) and vegetables (such as onions, tomatoes, potatoes and beans), both for West Africa’s coastal countries and for European countries. Onions are an especially valued export.

Burkina Faso is a historical country, mostly flat with a hilly area in the center of the country. The Northeast is the desert area. Tena Kourou, 749 meter, is the country’s highest peak. The area around Banfora is a popular tourist attraction with waterfalls, rock formations, and lakes. The country has 4 national parks, 1 UNESCO Biosphere reserve, 3 Complete Reserves, 6 Partial Reserves and 10 protected forests.
Burkina Faso is home to the largest elephant population in West Africa in addition to hippopotamus, buffalo, monkey, lions, crocodile, giraffe, and various antelopes.